Written by: IMQRScan Editorial Team, Last updated: December 2025
What is a QR Code and How Does It Work?
QR codes are now a common part of daily life. They appear on product packaging, restaurant menus, event tickets, advertisements, and payment screens. Their purpose is simple: to connect the physical world with digital information quickly and without manual typing.
This guide explains how QR codes work behind the scenes, how scanners read them accurately, and why businesses use them for fast, reliable access to information.
Although QR codes are traditionally black and white, they can be customized with brand colors, logos, and shapes.As long as contrast and spacing are maintained, customization does not affect scan reliability.
Because QR codes provide instant access without friction, they are widely used for marketing campaigns,customer engagement, reviews, and digital payments.
The Magic Revealed: How Do QR Codes Work
A QR code stores data in a two-dimensional grid rather than a single line like traditional barcodes.This allows it to hold more information and be scanned quickly from different angles.
When scanned, the device camera detects the QR code’s position markers, reads the data pattern,applies error correction if needed, and converts the pattern into readable information.
QR Code Structure Explained
A QR code is made up of specific visual elements that help scanners read it accurately. Each part has a defined role in positioning, alignment, and data decoding.
The significant elements in a QR code include:
- Data Cells: The small black/white modules where data is stored.
- Position Markers: Three corner squares that help orientation.
- Quiet Zone: Empty margin around the QR so scanners can detect it.
- Finder Pattern: The main locator pattern used to quickly find the code.
The scanner reads the pattern, applies error correction, and converts it into usable data.
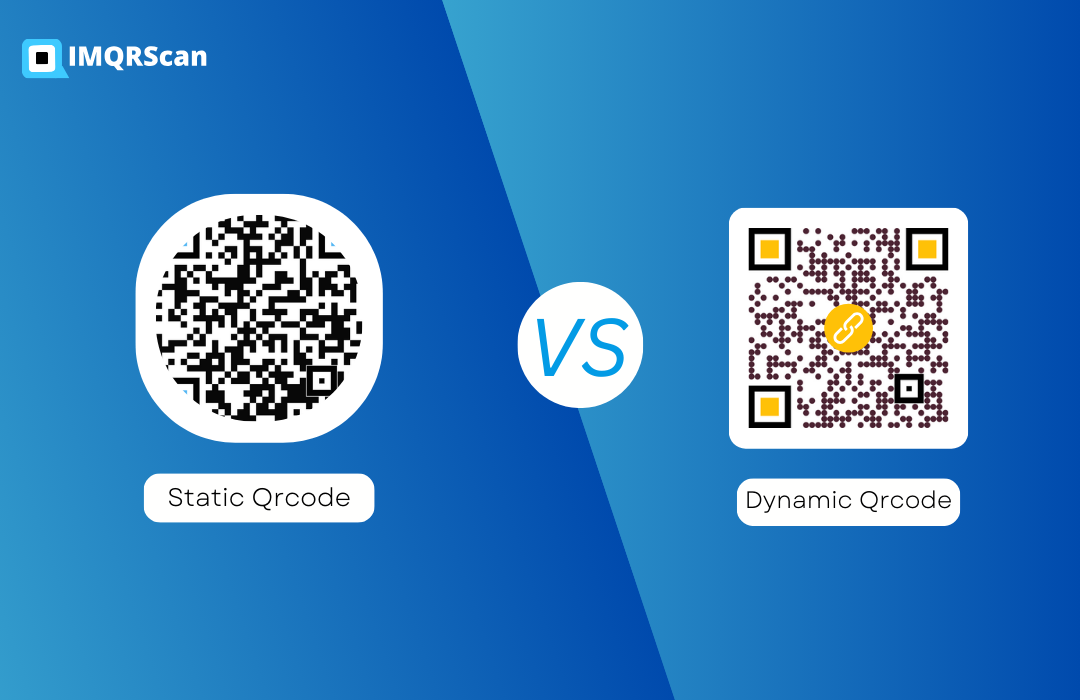
What You Should Know: Static and Dynamic QR Codes
Among other QR codes, static and dynamic codes are popular classifications. The difference between static and dynamic QR Codes relate to how they handle data.
- Static QR Codes:
- The static ones should be able to be saved for later, so they're not editable. That encoding lies in those specific codes is persistent, meaning you need a fresh QR code to change the content.
- Dynamic QR Code:
- Dynamic QR codes are more actionable because they mean you can change the content even post-generation. They tend to collect little data for a bounce to a more significant page, as slight as a link. Dynamic QR codes are something you can see, as they will be traceable, and you can update them immediately.
Business entities usually want dynamic QR codes to ensure better control and flexibility in tracking scans, including the chance to alter the destination without issuing new codes. With IMQRScan, dynamic QR codes let you update the destination link anytime and track scans by time/location/device.

Modern Business Strategies: The Power of QR Codes
Today, every business relies on QR codes for seamless, innovative customer engagement. From marketing to payment processing and customer service, QR codes revolutionize how companies communicate with consumers.
There are many things businesses can do with QR codes:
- Marketing Campaigns:
- Easily create QR code for ads, posters, and brochures to allow customers instant access to special offers or product details.
- E-commerce & Payments:
- Recently, businesses have widely embraced QR codes as a new digital payment method. Customers could use them to pay for an item or transfer money with a quick scan of the code.
- QR code payment:
- Event Ticketing QR codes solved all the boredom related to event tickets, with the receiver receiving a ticket digitally and scanning at the door.
- Customer Reviews:
- You can put Google Review QR codes on a receipt, package, or anywhere to make customers answer a survey or leave a review.
- QR codes act as frictionless entry points into digital content, turning a consumer experience into an interactive one.
Scanning and Accessing QR Code Information in a Simple Way
Scanning and getting a hold of QR code information is very simple; it is user-friendly for all technical backgrounds. So, here is how does a qr code work step by step:
- Open a QR Code Scanner:
- If your device doesn't have an inbuilt scanner, you can get one from the app store. Many smartphones even have a QR code scanner integrated into their camera apps.
- Scan the Code:
- Hold your device's camera towards the QR code. The camera should automatically detect the code and present you with the information decoded within.
- Tap the Result:
- Once scanned, tap the prompt to open the page, contact card, message, or payment request.All you need to do is follow the prompt that comes up.
- This quick, direct way of getting information has made QR codes incredibly popular and fruitful in many industries.






